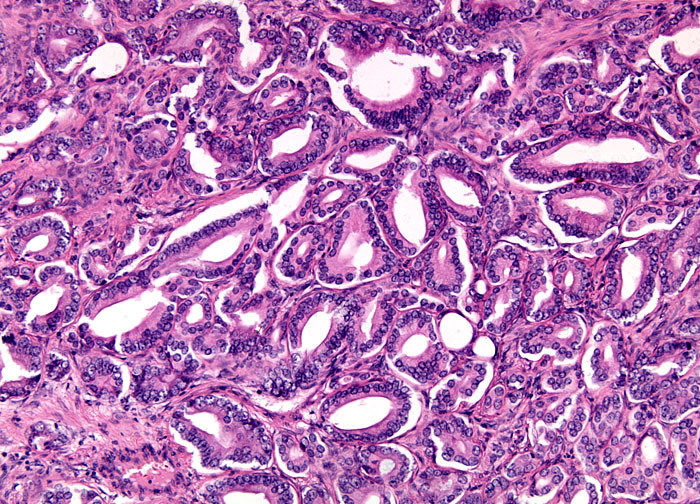
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia at 10x Magnification
Many men with benign prostatic hyperplasia experience urinary problems related to the condition. As the prostate enlarges, the gland places increasing pressure on the urethra, often resulting in difficulty beginning or ending urination, an inability to completely empty the bladder, decreased urine flow, and frequent urination. In the most severe cases, complete blockage of the urethra occurs, which may lead to kidney damage. The symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia are similar to those of several more serious problems, including prostate cancer, and should, therefore, be quickly brought to the attention of a medical professional. Several tests and procedures, including a digital rectal exam, prostate specific antigen blood test, rectal ultrasound, urine flow analysis, and cystoscopy, can enable the doctor to rule out other possibilities and make a definitive diagnosis of the condition.













