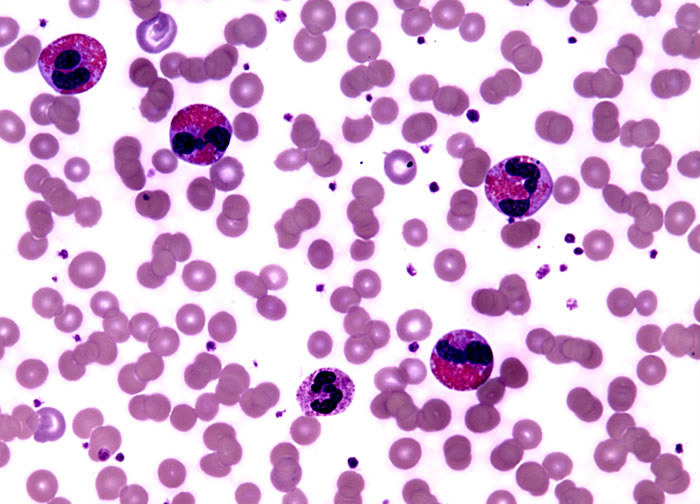
Eosinophilia at 40x Magnification
Eosinophils are members of the granulocytic class of white blood cells that function primarily in fighting infections of parasites and in allergic reactions. The cells, which are named for the eosin-staining granules they contain, generally comprise one to three percent of the total white blood cell count in a healthy individual. Persons who exhibit an abnormally large number of eosinophils are said to have eosinophilia. Though eosinophilia may be beneficial at times since the increase in white blood cells helps rid the body of certain parasitic invaders, the condition can also lead to tissue damage as an increasing number of eosinophils accumulate in the body. Asthma patients, for instance, often experience additional injury to the lungs due to eosinophilia.













