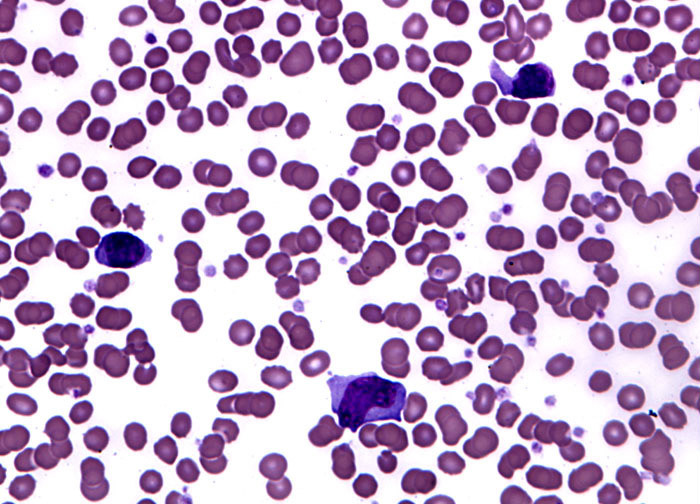
Mononucleosis at 40x Magnification
Infectious mononucleosis is a common viral disease often known simply as mono or the kissing disease that usually occurs in individuals between the ages of 15 and 35. The infection generally spreads via saliva exchange and is thought to be caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, a member of the herpesvirus family. Symptoms of mononucleosis are varied, but frequently include fever, fatigue, and sore throat. Swelling of the lymph nodes is also common and is the origin of another alternate name for the disease, glandular fever. Less often, a rash, eyelid swelling, or muscle soreness, as well as the more serious and even less common onset of pneumonia, meningitis, hepatitis, or peripheral neuritis, may occur. In some cases, the spleen may become enlarged, and rupture of the organ is the primary cause of the rare instances of death associated with mononucleosis.













