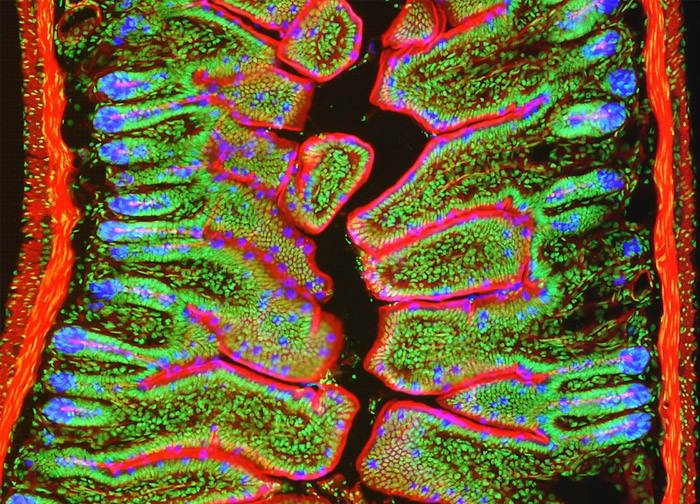
Mouse Intestine Tissue
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that selectively bind to specific configurations of sugar molecules. Certain oligosaccharide residues are found on cell surfaces and covalently linked to specific cellular components. Consequently, lectins can be utilized to identify various cell types and cell constituents. The lectin wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) binds to N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminic (sialic acid) residues and is frequently used to identify the Golgi complex. The mouse intestine tissue illustrated in the digital image above was labeled with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to WGA. The specimen was counterstained for F-actin and DNA with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin and SYTOX Green, respectively. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.













